If you’ve walked a farm field lately, chances are you’ve seen more than just crops. You might’ve spotted drones buzzing overhead, robots rolling through rows, or a tractor humming quietly without a driver in sight. This isn’t sci-fi—it’s the new reality of robotics use in agriculture. And if you’re leading an agritech operation or making investment decisions for your farm, you know the pressure is on: labor shortages, rising costs, sustainability demands… they all push you to do more with less.
That’s where robotic farming solutions step in. But here’s the thing: automation in agriculture doesn’t have to be complex or futuristic. There are already high-ROI agricultural robotics use cases working right now—and they’re ready to scale.
Let’s break down six of the most impactful robotics use in agriculture applications today.
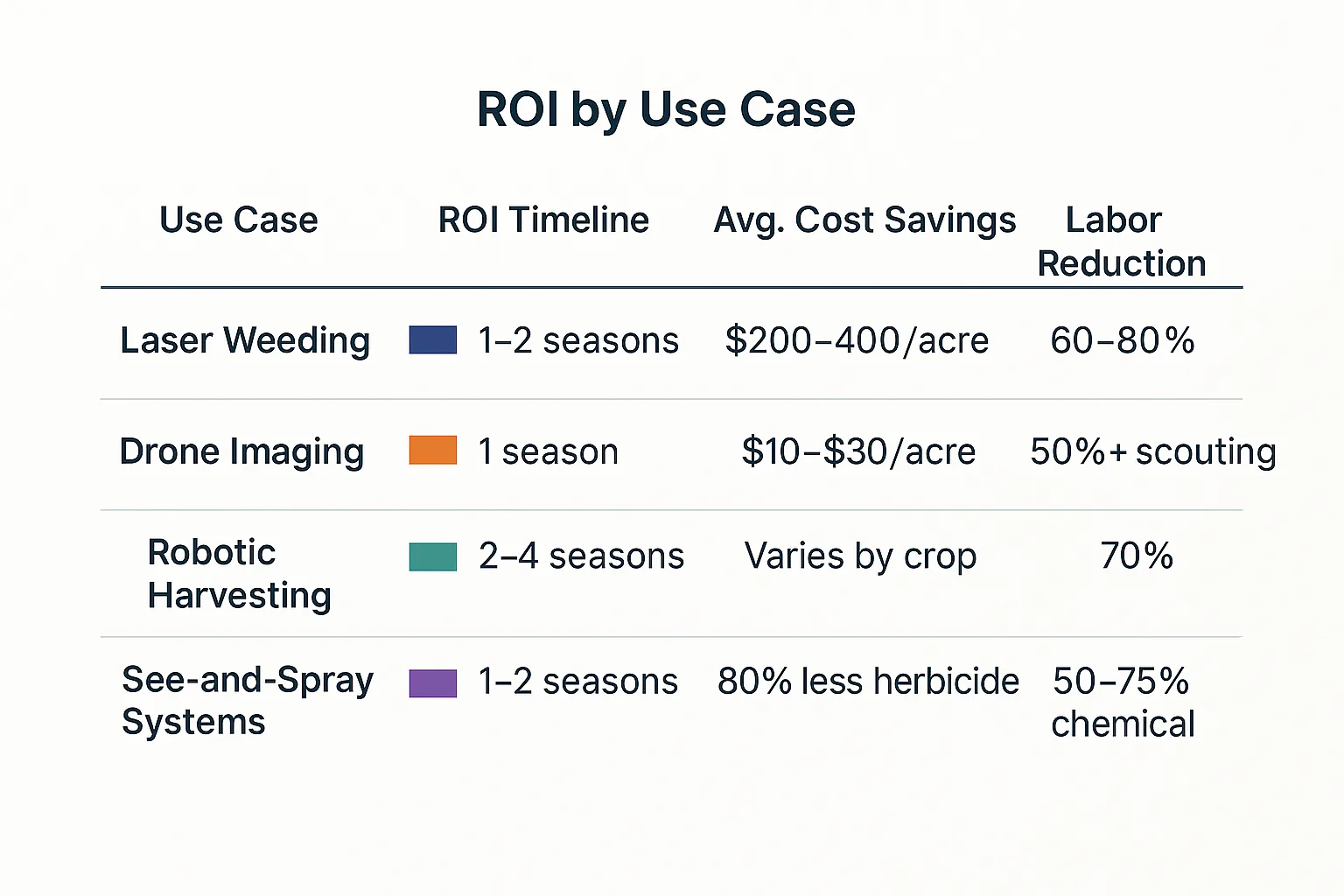
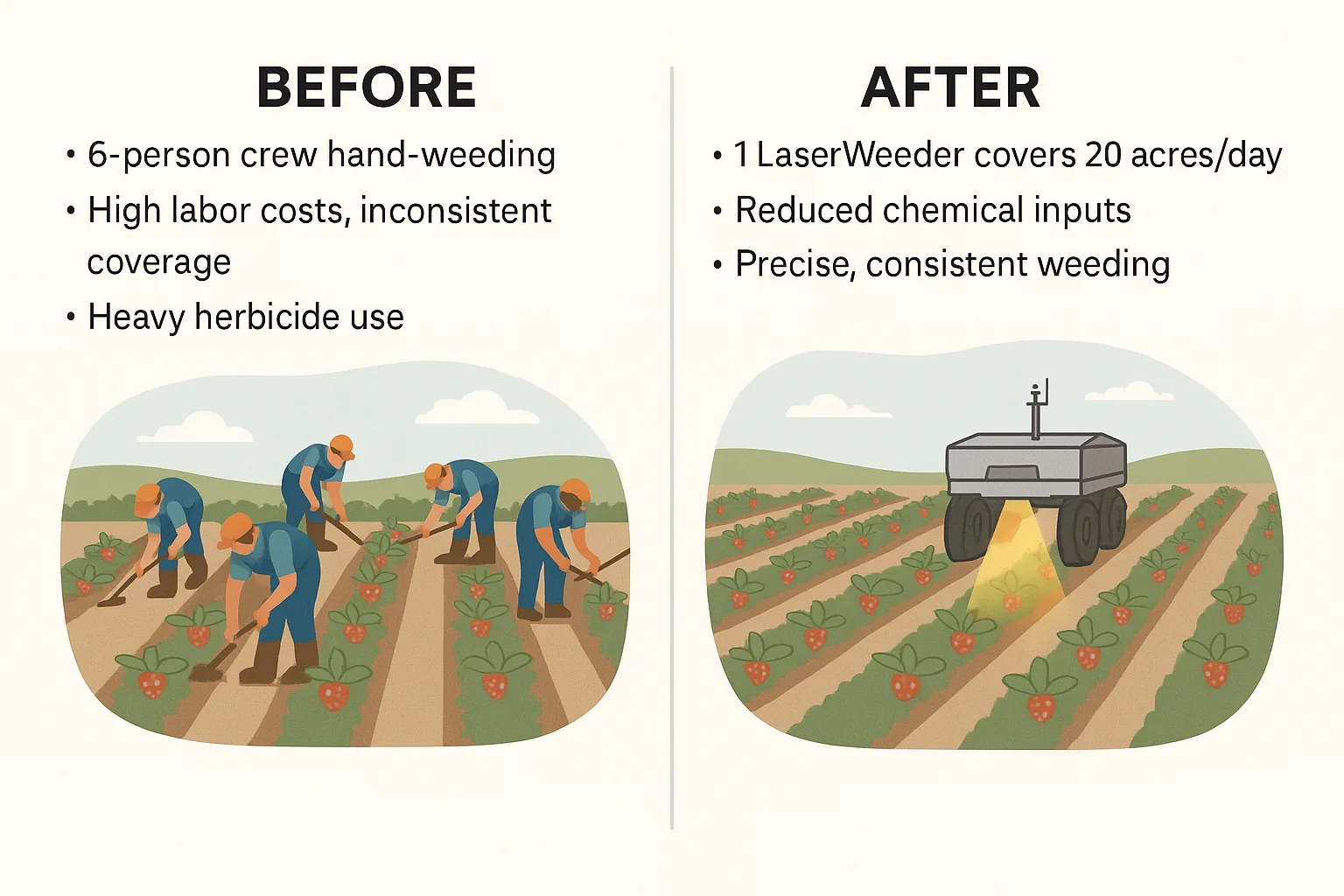
Laser-Focused Weeding That Cuts Costs and Chemicals
Weeding has always been one of farming’s most labor-intensive jobs. Now? Robots are zapping weeds with pinpoint lasers—and it’s saving serious money.
✅ How It Works:
Laser weeding robots like those from Carbon Robotics or Naïo Technologies use AI-powered cameras to identify and destroy weeds in real-time—no herbicides needed.
💰 The ROI:
- Cuts herbicide use by up to 80%
- Reduces hand weeding crews
- Pays back in 1–2 growing seasons in high-labor regions
🧠 Bonus:
These systems gather field data as they work—building a smarter picture with every pass, highlighting another level of AI in precision agriculture.
Vision-Guided Spraying: Only Spray What’s Needed
Traditional spraying treats every square inch the same. Vision-guided “see-and-spray” systems, like John Deere’s See & Spray Ultimate, are changing that.
✅ How It Works:
Cameras detect individual weeds or nutrient-deficient plants, and sprayers deliver a precise dose of treatment.
💰 The ROI:
- Up to 90% reduction in chemical use
- Savings of $25–$30 per acre
- Faster ROI (12–18 months) on mid-sized farms
🌎 Bonus:
This targeted approach supports environmental goals and fits seamlessly into modern farming technologies.
Robotic Harvesting: Gentle, Precise, and Always Available
Labor shortages during harvest season? Meet your new team.
✅ How It Works:
Robotic harvesting systems with grippers or suction arms pick delicate crops without bruising them.
Examples:
- Tevel Aerobotics: Flying fruit pickers
- FFRobotics: Multi-arm ground harvesters
💰 The ROI:
- Reduces seasonal labor costs by up to 50%
- Operates 24/7—even at night
- Improves yield through optimal harvest timing
🚜 Real-World Wins:
California growers have reported early success using robotic strawberry pickers, demonstrating the real-world power of robotics use in agriculture.
Drone Imaging for Scouting, Stress, and Strategy
Aerial insights are reshaping how growers manage fields.
✅ How It Works:
Drones with multispectral sensors detect early signs of stress or disease. AI turns the data into precise field maps.
💰 The ROI:
- Save $10–$15/acre in scouting costs
- Targeted inputs reduce waste
- Early detection means healthier yields
📦 Agricultural Drone Applications:
- Rice: Monitor water zones
- Corn: Spot nitrogen deficiency
- Vineyards: Detect irrigation needs
This is one of the fastest-growing agricultural robotics use cases—particularly when paired with drone spraying in agriculture for a full-spectrum solution.
Aerial Spraying and Seeding: Reach the Tough Spots
Drones are stepping beyond scouting and into action.
✅ How It Works:
Precision drones apply seeds, fertilizer, or pesticides in areas that tractors can’t easily reach.
💰 The ROI:
- Saves labor and machinery costs
- Avoids soil compaction
- Ideal for hillsides, orchards, or wet fields
🚧 U.S. Update:
FAA regulations are evolving, but drone spraying in agriculture is gaining ground, especially for specialty crops. This is another way robotics use in agriculture is adapting to terrain challenges.
Smart Irrigation and Greenhouse Automation
Water efficiency is more critical than ever.
✅ How It Works:
Greenhouse automation systems and smart irrigation tools use real-time data to manage moisture, light, and temperature.
💰 The ROI:
- 20–30% water savings
- Less manual labor
- Higher crop consistency
🌍 Bonus:
Great for water-scarce areas and high-margin crops. Farm automation ROI is especially visible here through resource savings and consistent production.
These technologies aren’t futuristic—they’re delivering real-world results today. The most effective robotics use in agriculture meets your current challenges head-on: labor shortages, cost pressures, and sustainability goals.
Whether it’s autonomous tractors, weeding lasers, drones, or harvest bots, the best strategy is to adopt where the ROI is clearest—and scale up.
At the end of the day, investing in robotics use in agriculture isn’t just about automation. It’s about building resilience, unlocking growth, and future-proofing your farm.
How Beam Data Helps Power the Future of AgriTech
Beam Data supports the seamless deployment and scaling of robotics use in agriculture by providing the infrastructure to manage robotics fleets, process agricultural data in real-time, and integrate with existing farm systems. Whether you’re deploying drone spraying in agriculture, managing greenhouse automation systems, or piloting robotic harvesting systems, Beam Data ensures your technology runs reliably, securely, and efficiently—helping you maximize your farm automation ROI and scale smarter.
FAQs: Robotics in Modern Farming
1. What’s the cost to implement agricultural robotics?
Solutions range widely—from $2,000 for basic drones to over $100,000 for harvesters. Robotics-as-a-Service (RaaS) options make adoption easier for many.
2. What kind of ROI can I expect?
Use cases like laser weeding or targeted spraying typically pay off in 1–2 seasons. Farm automation ROI is highest in labor-intensive tasks.
3. Are these tools only for big farms?
No. From small drone kits to scalable weeding bots, many robotics use in agriculture solutions work for smaller farms too.
4. Can they integrate with my current systems?
Yes—many platforms support APIs and work with farm management software.
5. Which crops benefit most?
Fruits, vegetables, and greenhouse crops gain the most initially, but row crops like corn and soy are increasingly benefiting from modern farming technologies.

